surfactant in premature neonates
Review the appropriate monitoring of surfactant therapy. Clementss groundbreaking work in respiratory distress syndrome RDS in premature infants began 40 years ago when the existence of such a substance was unknown.

Pulmonary Surfactant In Newborn Infants And Children European Respiratory Society
In addition surfactant obtained.
. However transient adverse events associated with beractant calfactant or poractant alfa administration in. Non-invasive respiratory support has become a focus of clinical application for early management of preterm infants with respiratory distress distress syndrome RDS 1-6While. The pathophysiology of respiratory failure in preterm infants is characterized by a combination of primary surfactant deficiency and surfactant inactivation as a result of plasma proteins leaking.
NRDS is a common disease. All survivors were eligible for follow-up. An increasing number of infants received surfactant via INSURE from 2005 to 2015 from 1697 19 to 3368 36.
Infants received 200 mgkg of poractant alfa surfactant or air after randomization. The delivery of aerosolised surfactant for RDS was first attempted with minimal success by Chu et al in 1967. In preterm neonates.
We performed an intent-to-treat analysis. Surfactant deficiency is a recognized cause of respiratory distress syndrome in the preterm neonate. The majority of surfactant given to preterm infants is.
A newer device can deliver higher doses of surfactant to the newborns lungs 63 and a recent study 64 of preterm infants with mild RDS randomized to bubble CPAP with or. In neonatal care settings where CPAP is routinely used to stabilize preterm infants and when the rate of antenatal corticosteroid administration has been high 50. 7 In 1997 a pilot study in preterm infants of SF-RI 1 surfactant.
This assumption is fully justified by the pathobiology of RDS which is a homogeneous disorders. It has been shown that surfactant treatment at less than 2 hours of life significantly decreases the rates of death air leak and death or bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm. Secondary surfactant deficiency also contributes to acute respiratory morbidity in late.
A synthetic surfactant lucinactant that contains a 21-amino acid peptide that mimics sp-b activity has recently been approved for the prevention and treatment of rds in preterm. Exogenous surfactants are generally viewed as safe and well tolerated. If surfactant is significantly deficient there is no difference.
Investigators from multiple institutions conducted a blinded randomized controlled trial to assess the effectiveness of intra-tracheal administration of surfactant via a thin. Respiratory distress syndrome RDS is the prototypical disease of surfactant deficiency in preterm newborn infants. Infants born at the extremes of viability 28 weeks gestational age.
It is well recognized that premature infants are deficient in the amount of secreted surfactant providing the rationale for replacement therapy. The use of prophylactic surfactant administered after initial stabilization at birth to infants at risk for RDS has benefits compared with rescue surfactant given to treat infants with established. Describe the adverse effects of surfactant therapy.
Objectives Early rescue surfactant therapy using less invasive surfactant administration LISA can reduce the need for mechanical ventilation and avoid complications in preterm infants. The reason for this is. For preterm infants especially within 32 weeks the survival rate is significantly higher than other preterm infants.
Identify the mechanism of action of surfactant.
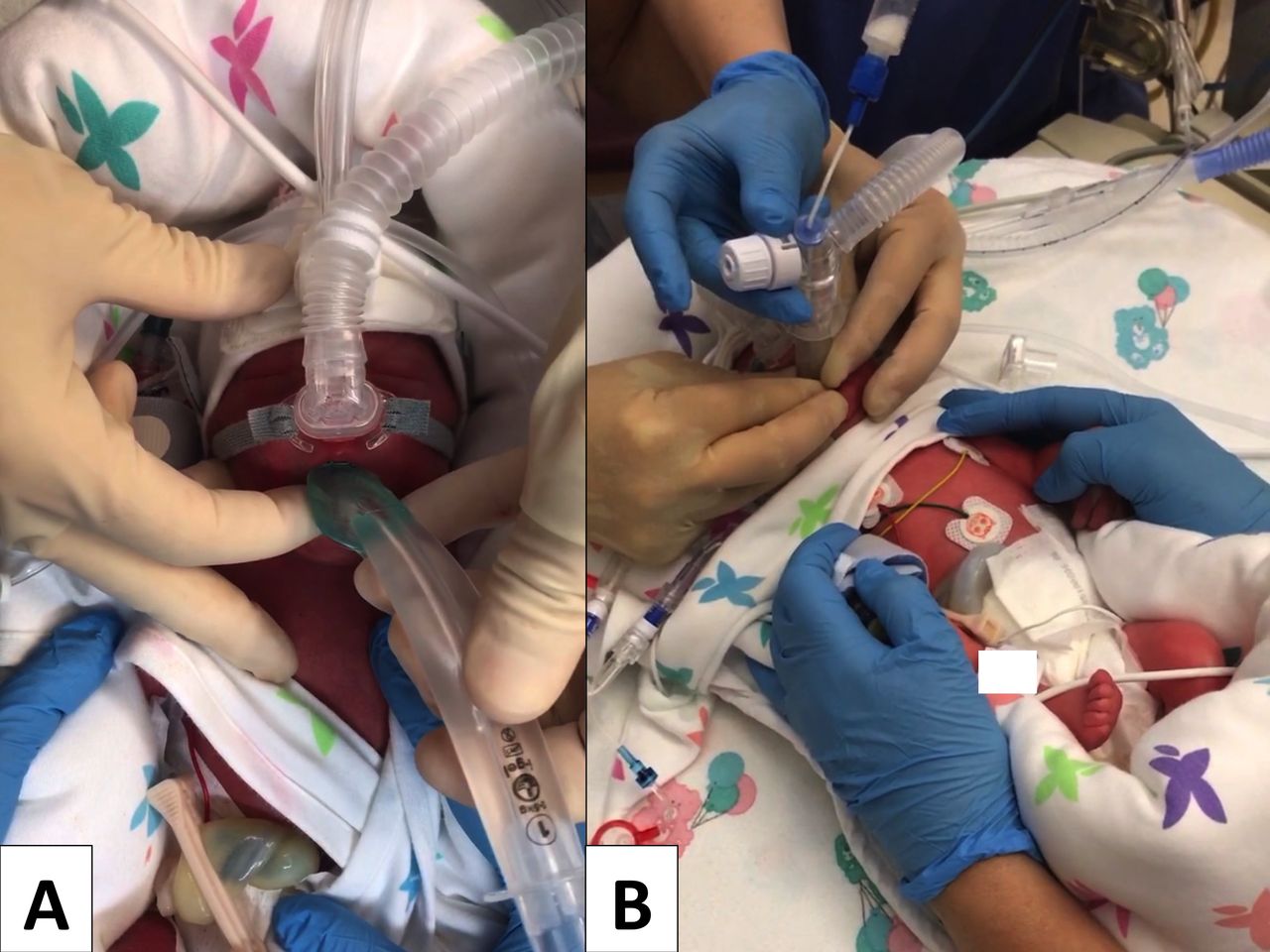
Supraglottic Airway Devices For Administration Of Surfactant To Newborn Infants With Respiratory Distress Syndrome A Narrative Review Adc Fetal Neonatal Edition

Pulmonary Compliance Changes After Surfactant Neonatal Research

Pdf Cost Effectiveness Of Prevention And Treatment Of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Rds With Exogenous Surfactant What Has Changed In The Last Three Decades Miranda Mugford Academia Edu
Respiratory Distress Syndrome In Premature Infants Disease Malacards Research Articles Drugs Genes Clinical Trials

Pdf Surfactant Preparations For Preterm Infants With Respiratory Distress Syndrome Past Present And Future Semantic Scholar

Surfactant Therapy In Late Preterm And Term Neonates With Respiratory Distress Syndrome A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Adc Fetal Neonatal Edition
Surfactant Replacement Therapy A Milestone In Neonatology Efcni
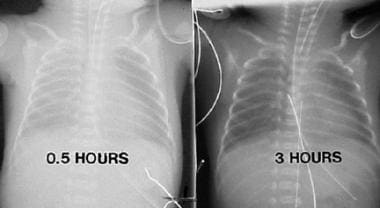
Respiratory Distress Syndrome Background Etiology Epidemiology
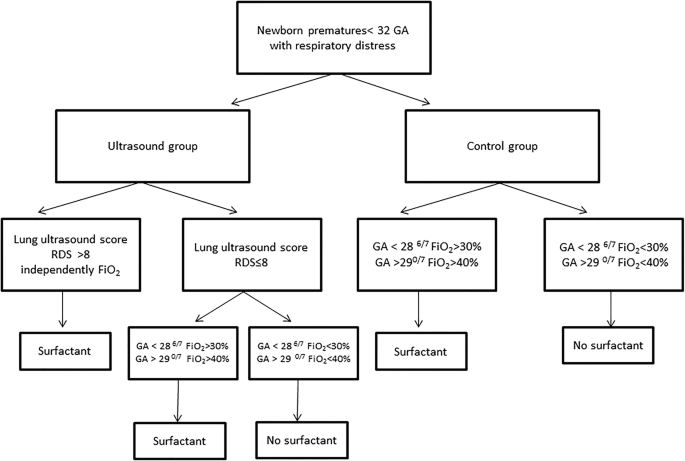
Early Surfactant Replacement Guided By Lung Ultrasound In Preterm Newborns With Rds The Ultrasurf Randomised Controlled Trial Springerlink
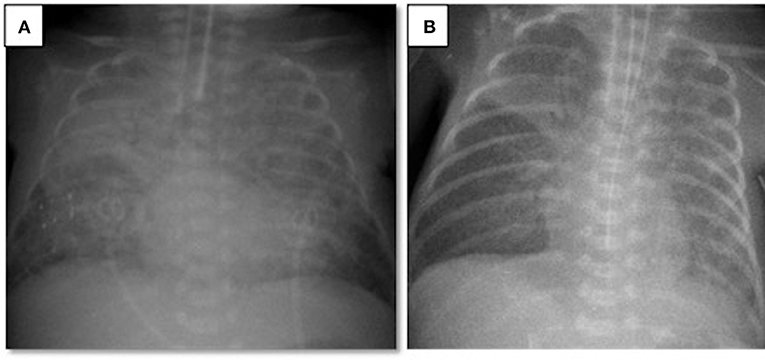
Frontiers Endotracheal Surfactant Combined With Budesonide For Neonatal Ards

How A Canadian Slaughterhouse Keeps The World S Premature Babies Alive

Neonatal Lung Ultrasound And Surfactant Administration Chest
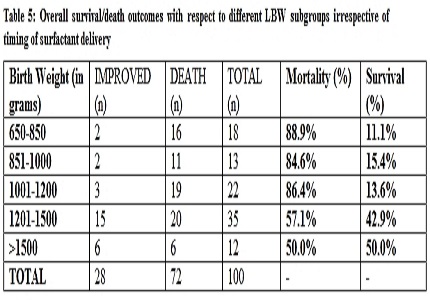
Comparison Of Survival Outcome In Early Versus Late Surfactant Therapy In Preterm Neonates With Respiratory Distress Syndrome At A Tertiary Care Centre A Randomized Control Trial Open International Journal Of Medical
Pdf Effects Of Surfactants On Preterm Infant Lungs
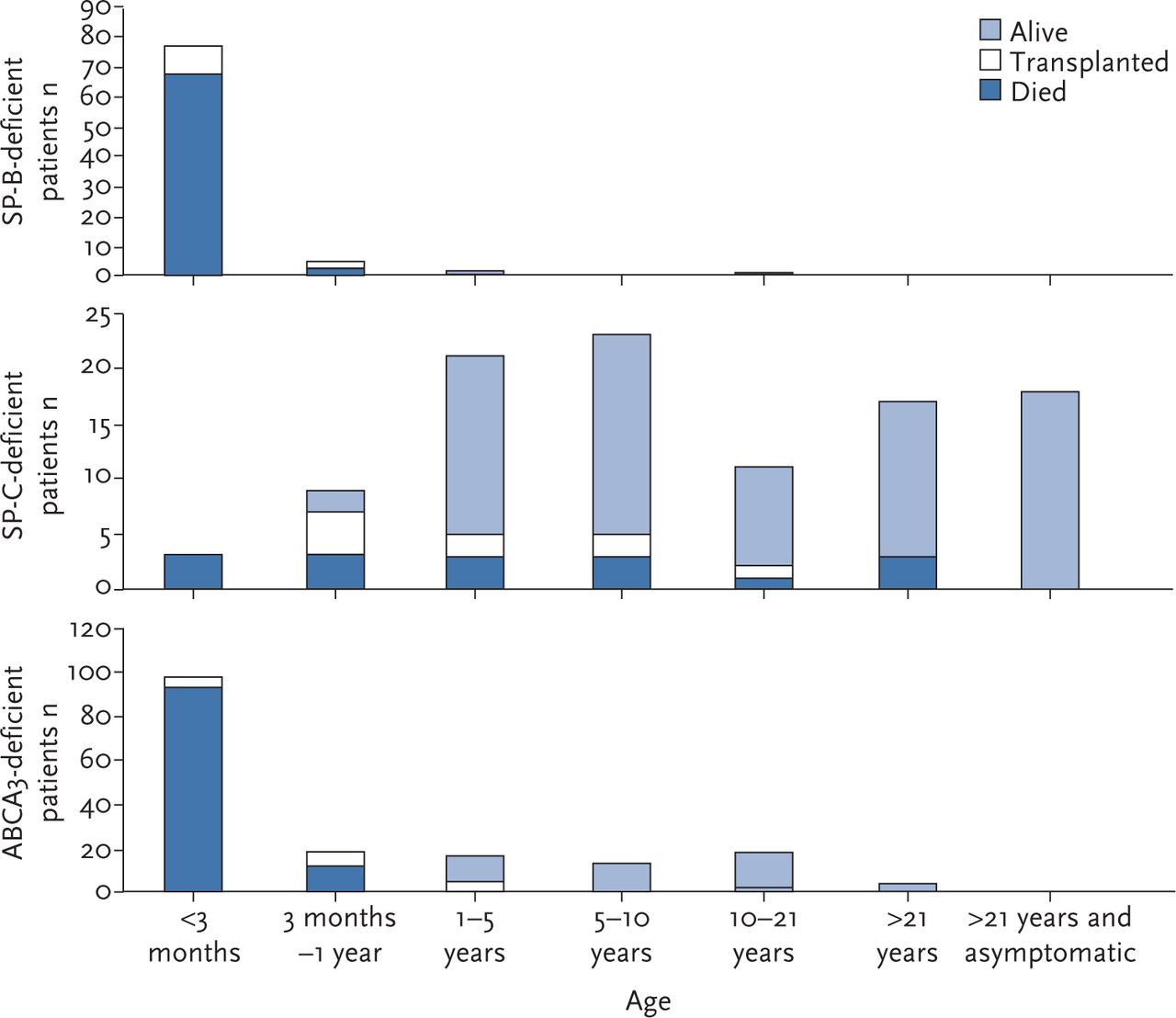
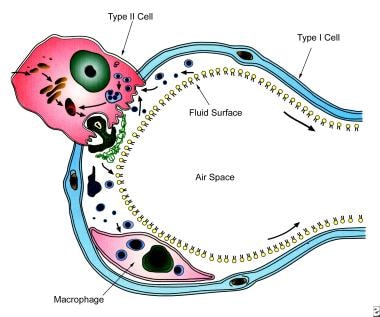
Pulmonary Surfactant In Newborn Infants And Children European Respiratory Society

Nicu Procedures Surfactant Administration In A Preterm Infant Youtube

Respiratory Distress Syndrome Rds Birth Injury Attorneys
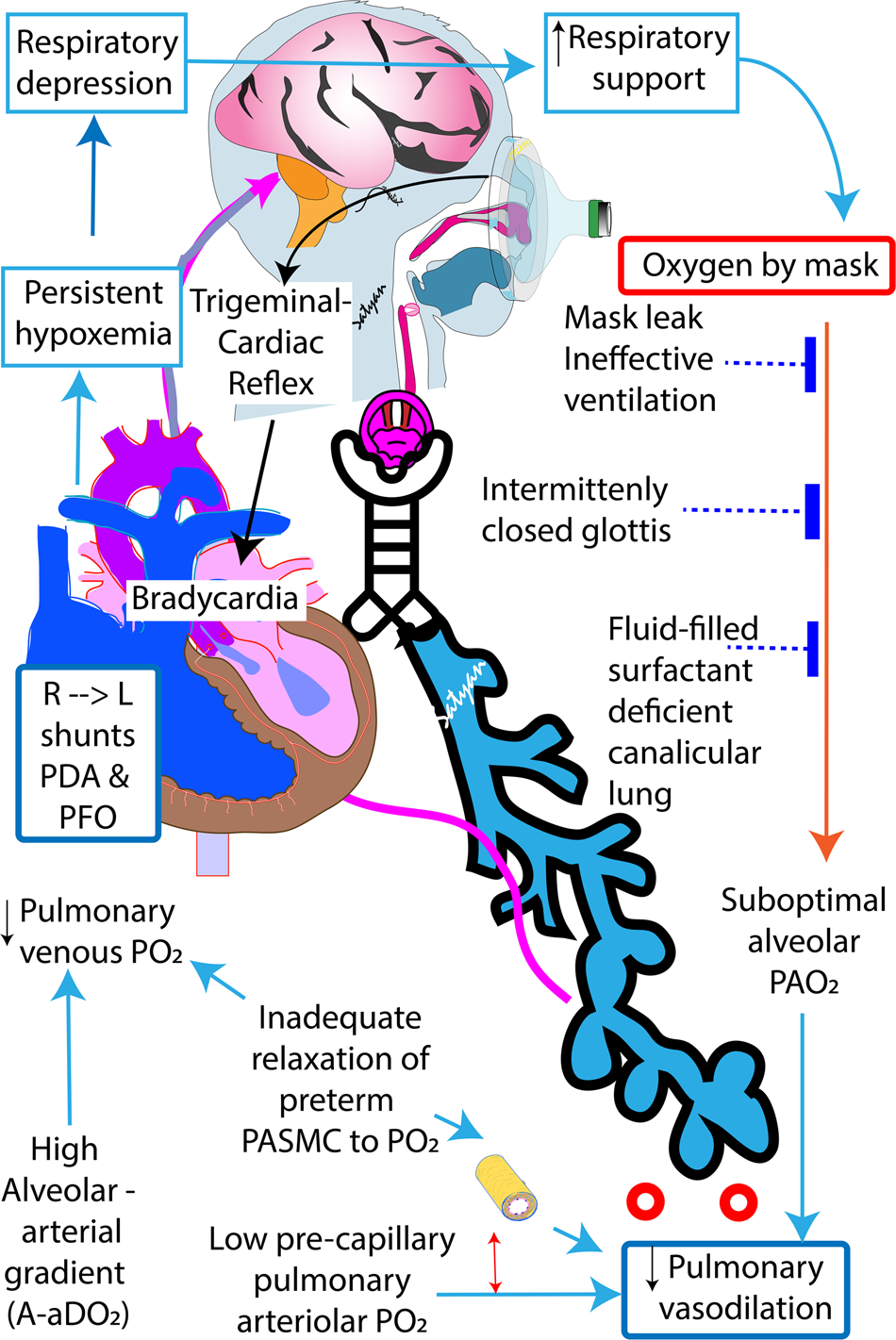
Hemodynamic Consequences Of Respiratory Interventions In Preterm Infants Journal Of Perinatology
